Logistics
How to Solve Last Mile Delivery Challenges with Technology

Last mile delivery is always the make-or-break step for businesses. At this stage, customers either have a positive experience and recommend a brand to their friends or have a negative experience, and all the other stages are history. One could think that delivering products from point A to B would be straightforward, but there are multiple challenges along the way that threaten your client's satisfaction.
It's the crucial final leg of the journey, where goods make their way from a distribution center to their ultimate destination, whether it's a customer's doorstep or a retail store shelf. However, the last mile is often the most complex, costly, and challenging part of the delivery process.
In this post, we'll uncover the intricacies of the last mile, define its significance in today's fast-paced business landscape, and delve into the strategies and technologies that can help you optimize this critical phase of your supply chain.
What Is Last Mile Delivery and What Makes It Such a Challenge?
The culmination of your business's product journey, known as last mile delivery, involves transporting goods from your base or transportation hub to the end user's doorstep. However, this final step poses a distinct challenge known as the "last mile delivery problem," primarily because it tends to be the costliest phase, often accounting for over half of the total shipping expenses.
Unlike bulk shipments to a single destination, last mile delivery involves dispatching numerous smaller packages, each with its unique endpoint. This is at the heart of the last mile challenge—more destinations translate to intricate routes, increased idle time, and extended hours on the road. Consequently, it necessitates maintaining a larger fleet of delivery vehicles and drivers to transport relatively few products. Furthermore, certain products may require inside delivery, adding an extra layer of complexity to the process.
How Much Does Last Mile Delivery Cost?
The most costly segment within the fulfillment chain is unquestionably the last mile delivery, which is between $10 and $50 per package—trending toward the higher end for heavy items. For comparison, failed deliveries cost an average $17.20 per instance.
However, even when exclusively dealing with smaller packages, executing last mile deliveries can prove costly, especially without the advantage of scale. The typical wage for a delivery driver stands at $18.53 per hour, and additional expenses like warehousing, fuel, and vehicle maintenance must also be considered.
When you're facing a minimum $2 loss with each delivery, the challenges posed by the last mile delivery problem become acutely evident. These figures underscore the imperative for drivers to accomplish multiple deliveries per hour in order to sustain and nurture your business's growth.
Why Is It So Expensive?
Managing the delivery of thousands of packages to their ultimate destinations on a daily basis poses a multifaceted logistical challenge. The intricacies of last mile fulfillment are compounded by various contributing factors, each impacting the overall cost.
Reduced Average Speeds and Fuel Efficiency: When delivery drivers navigate through a city, they contend with local roads, causing a significant drop in the average speed and fuel efficiency. Smaller delivery vehicles typically average 6.5 miles per gallon (MPG) at a steady speed of 55 miles per hour. However, urban deliveries rarely achieve this speed, as frequent deceleration, stops, and acceleration take their toll, both on average speeds and gas consumption.
Increased Stops Result in More Idling and Downtime: Urban deliveries entail extensive idling due to traffic lights, diverse road users, and complex street layouts. On average, an idling delivery truck consumes 0.84 gallons per hour. Moreover, the driver's time must be compensated, regardless of whether they are moving or stationary.
Challenges with Failed Deliveries: Unlike distribution to fulfillment centers or supply chain partners, final customer deliveries come with a significant risk of failed deliveries. On average, a single failed delivery incurs a cost of $17.78, and a startling 5% of all last mile deliveries result in failure. Factors contributing to this issue include unexpected deliveries without prior notice, late deliveries, lack of delivery scheduling options, and address errors.
Complex Routes Lead to Increased Out-of-Route Miles: Managing a large number of individual stops can lead drivers to inadvertently deviate from their designated routes, accumulating unnecessary miles. Research indicates that out-of-route miles can make up as much as 10% of a delivery fleet's total mileage.
Returns, Refunds, or Discounts: E-commerce products experience an average return rate of 20%, posing a significant challenge in e-commerce fulfillment. Businesses selling consumer products online should anticipate that one in five customers will request returns, refunds, or exchanges, leading to additional costs and logistical complexity.
Even though it's the last step, last mile delivery accounts for over 41% of the total delivery cost. This paradoxical cost distribution underscores its undeniable significance in the intricate web of supply chain management, so these multifaceted challenges and cost factors demand meticulous planning and strategic solutions to ensure cost-effective and efficient operations.
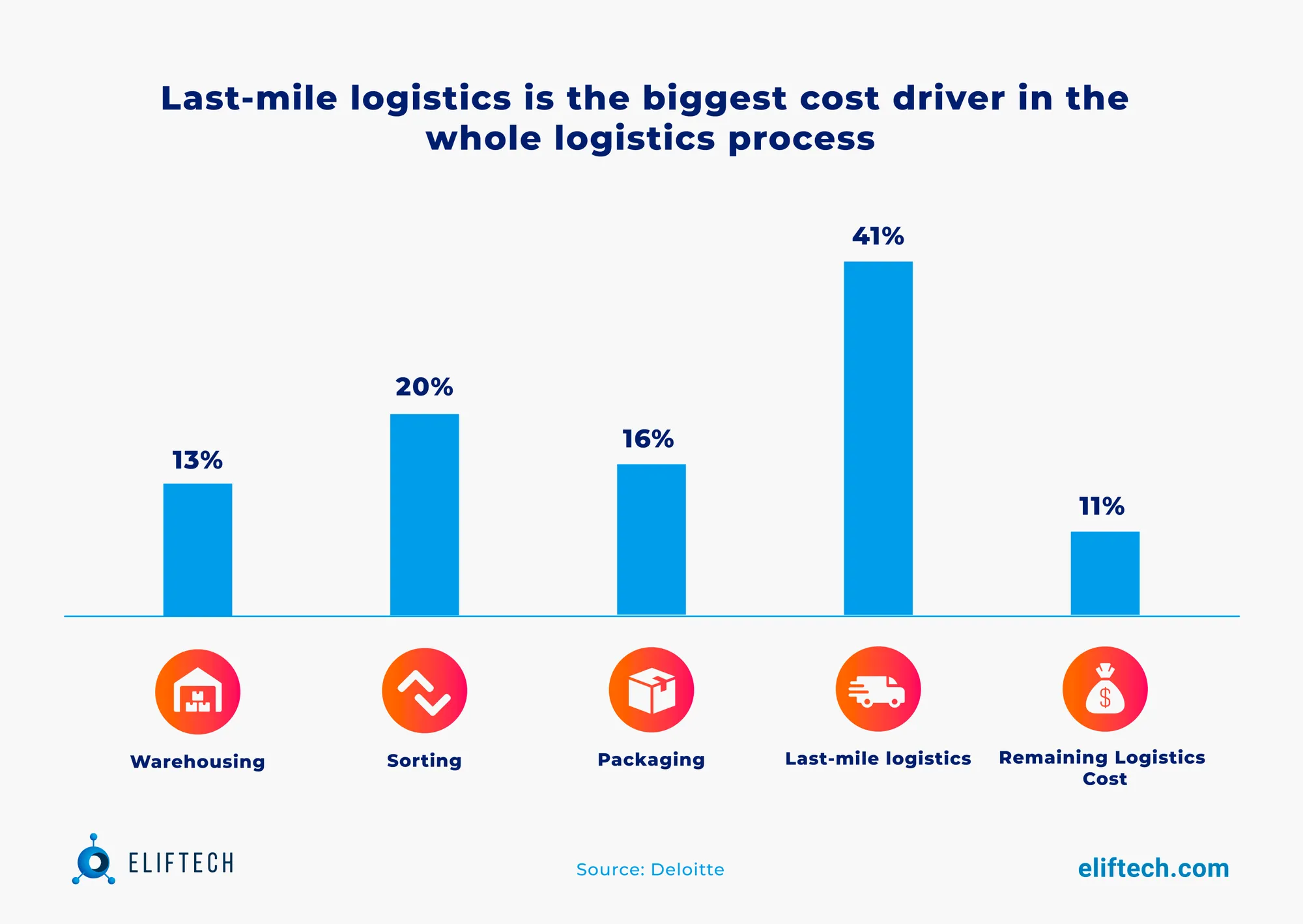
Furthermore, modern businesses must not only meet but surpass customer expectations compared to competitors. That’s why worldwide logistics corporations like Meest International and online retailer Amazon direct their efforts toward streamlining the entire supply chain process in a manner that minimizes transit time and maximizes customer satisfaction. And they see no way better than doing it through last mile delivery innovation and delivery chain reformation.
Increasing Demand for Last Mile Delivery
Navigating through the swiftly changing consumer behavior and the resulting fluctuations in demand patterns, it quickly becomes clear that this isn't just a fleeting phase but rather a distinct shift in the business landscape. However, there are a few other crucial factors that have increased the significance of last-mile delivery in 2023 and beyond. Let’s explore the implications of this surge.
#1. E-commerce boom
Online shopping has become a preferred method for purchasing a wide range of products, from electronics to groceries, and customers expect swift delivery to their doorsteps. Just for illustration, 75% of European-based customers purchasing goods or services online reflect their expectations for the need for quality deliveries clearly.
The e-commerce industry is, in turn, rapidly expanding due to the rising population density and urbanization, widespread use of smartphones and tablets, increased internet access, the growing adoption of digitalization and online payment methods, faster purchasing options, lower costs, time savings, and overall convenience it offers.
#2. The shift of the e-commerce market to the B2C segment
The shift of the e-commerce market to the B2C (Business-to-Consumer) segment has also greatly contributed to the increase in demand for last-mile delivery. Unlike the traditional B2B (Business-to-Business) model, the B2C model involves delivering smaller quantities of products directly to end consumers.
As businesses now cater to individual customers, they must meet the expectations of consumers who seek fast and seamless delivery experiences. This growing trend in the e-commerce market has prompted companies to adapt their logistics strategies with a greater focus on optimizing last-mile delivery efficiency.
#3. Same-day and next-day delivery models
In the realm of modern-day commerce, customers don't just enjoy —they insist on— rapid deliveries. Capgemini's research indicates that a two-hour delivery option could enhance loyalty for 55% of customers, rising to 61% for same-day delivery. However, when delivery extends beyond three days, only 30% find it loyalty-boosting, likely due to its commonality. Surprisingly, merely 19% of businesses offer two-hour or faster delivery.
Seizing this opportunity can set industry leaders apart, aligning with customer expectations and driving loyalty. Moreover, the link between customer satisfaction and rapid delivery becomes even more pronounced when considering the willingness to pay more for this value-added service. Satisfied customers are willing to invest more, paying 4.9% of the total order value for a two-hour delivery. Yet, this willingness slightly drops to 4.3% for those who aren't satisfied.
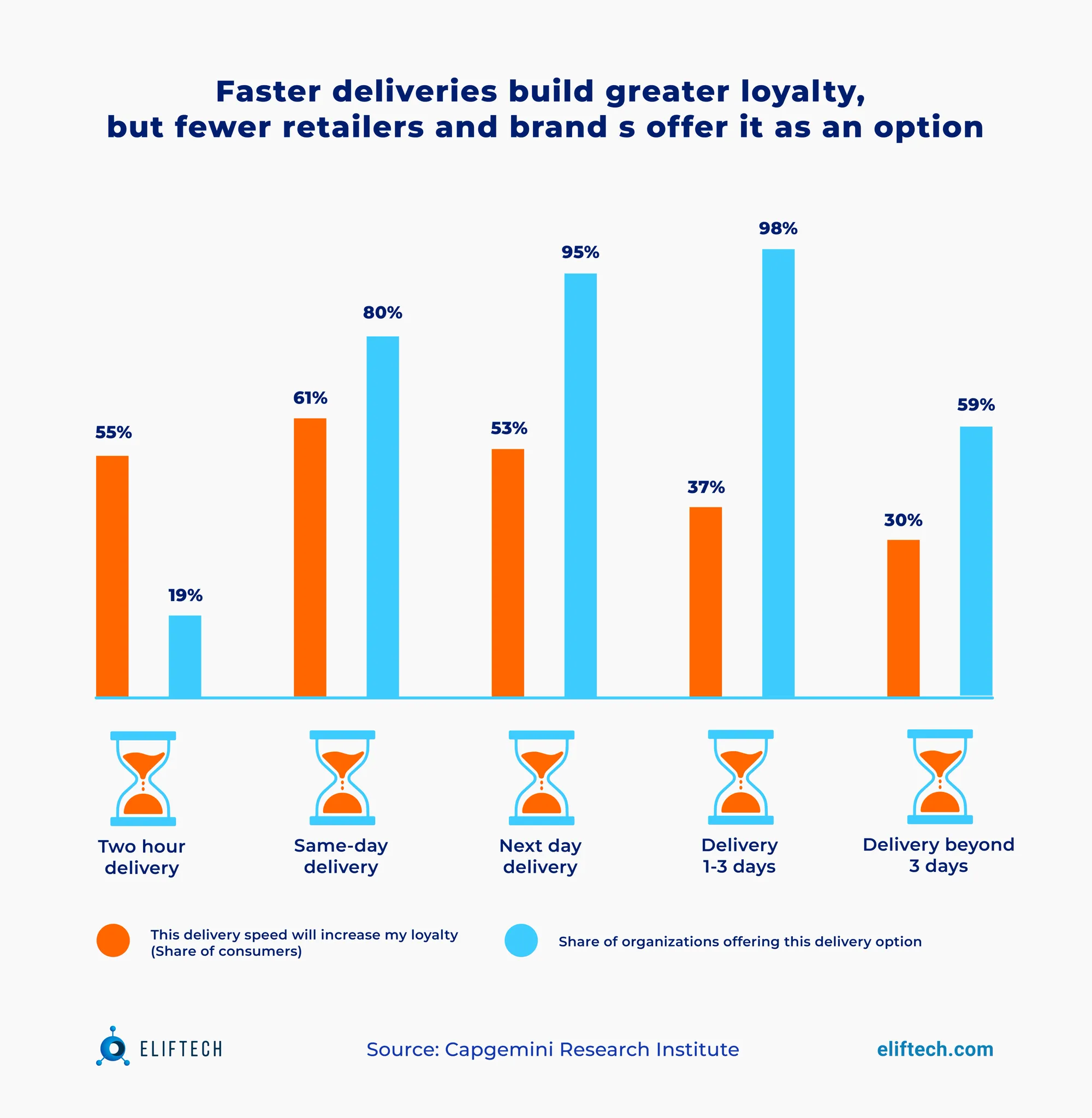
In response to these expectations, businesses face pressure to optimize their logistics and last-mile delivery operations. This gives rise to specific concerns:
- Retailers question covering service costs
- Customers hesitate due to shipping fees
- Increased risk of shopping cart abandonment.
- Businesses struggle to meet fast delivery demands
#4. The varied range of products with specialized needs
As e-commerce steadily grows, the variety of goods delivered to the customer's doorsteps is also increasing. This includes not only regular items but also specialized products such as temperature-sensitive ones.
For instance, items such as perishable foods and pharmaceuticals necessitate temperature-controlled transportation to maintain their quality during transit. Efficient last-mile logistics ensure the punctual delivery of time-sensitive products to customers or designated destinations, precisely when needed.
#5. Competitive market
Statistically, if the estimated shipment time is significantly prolonged, approximately 32% of global shoppers choose to abandon their carts. The exponential growth of online retailers and marketplaces has cultivated an intensively competitive environment. With a multitude of e-commerce ventures launching daily, the provision of exceptional delivery services becomes a pivotal strategy in carving a unique niche and capturing attention.
In light of this, elevating the last-mile delivery process surfaces as a critical element for differentiation and a novel pathway to establish unwavering customer loyalty.
Last Mile Delivery Challenges
Last-mile delivery distinctly differs from bulk shipping and distribution. It involves the transportation of numerous individual packages, each bound for a unique destination. This creates a complex web of travel routes and prolonged road time, defining the key facets of what can be recognized as the 'last mile delivery problem.' It is indeed a herculean task to manage.
Businesses, therefore, inherently face a crucial need to maintain a significant delivery fleet and driver roster or seek sophisticated last mile delivery route optimization strategies to mitigate this intricacy.
Below, we've shed light on some key factors that catapult costs and hamper efficiency in last-mile delivery:
The complex web of logistical challenges
Last-mile delivery drivers transport multiple packages to several locations within a city, facing a labyrinth of roads and various driving conditions. Increasingly, businesses must tackle unpredictable challenges to keep up with the demands of this intricate logistics landscape.
These hurdles include adverse weather conditions, traffic congestion, parking constraints, and unforeseen traffic bottlenecks. Each factor serves as a potent catalyst for substantial delays in delivery timelines, thereby increasing operational costs.
Frequent stops and idling time affect delivery efficiency
When drivers must divide their time between various destinations, which not only results in delays but also contributes to greater fuel consumption. With drivers spending more time on the road, businesses must account for these labor costs, whether the drivers are moving or stationary.
These challenges underpin the necessity for strategic planning and effective management in the world of last-mile delivery to optimize time, resources, and costs.
Increased e-commerce demand in urban centers
Many factors, such as urban population growth, changing consumer preferences, and the convenience of online shopping, are driving the growth of e-commerce demand in urban areas.
As cities become epicenters of economic activity and residential hubs, more people are choosing to shop online, resulting in a surge in last-mile deliveries. Moreover, nearly 78% of deliveries will take place in urban areas by 2030. This highlights the importance of a fast last-mile solution to maximize daily delivery capacity and efficiency.
Returns and failed deliveries
Last-mile delivery encompasses the complexities of handling returns and failed deliveries, averaging about 17.2 U.S. dollars in additional costs. Reasons behind these returns could stem from customers changing their minds, receiving damaged products, or experiencing issues with their purchase. Failed deliveries arise when customers are unavailable at the delivery address or when the provided address is inaccurate.
The repercussions of returns and failed deliveries manifest in increased expenditures due to higher labor demands, transportation costs, and potential dips in customer satisfaction. Consequently, prioritizing shipping accuracy takes on paramount importance, especially in e-commerce, where the overall shipping experience directly influences customer satisfaction.
Parcel size and weight
Delivery staff can handle a variety of products, ranging from small parcels to oversized items. Small packages may be easier to handle, but larger, heavier items can be problematic.
Large shipments often require specialized equipment and may require a large number of delivery workers to ensure safe and efficient handling. Also, larger parcels can take up more space in delivery vehicles, potentially reducing the number of parcels that can be delivered in one trip, impacting vehicle usage and overall delivery efficiency. So, these factors also contribute to increased costs and logistical complexities in the last-mile delivery process.
Consumers expect more transparency and personalization
Today's consumers expect heightened transparency, particularly regarding their deliveries in transit. The acceptance of unforeseen deliveries has significantly dwindled, adding another layer of complexity and cost to the last-mile delivery process.
Influenced by global delivery services giants like Uber and Meest, retailers are expected to mirror these strategies and cultivate a transparent delivery process that caters to consumer expectations. Meeting these expectations is no longer a choice for businesses but a strategic necessity in today's competitive e-commerce landscape.
ElifTech has completed a project on creating a fleet management system that offers fleet metrics, maintenance planning, immediate notifications, and real-time analytics, along with real-time location status of vehicles. Our contribution to the project allowed our client to reduce costs and improve the efficiency of fleet management significantly. This, in turn, allows more control over how and when items are delivered, translating to improved, personalized customer experience.
Key Strategies for Optimizing Last Mile Delivery
Last-time is a wonderful opportunity for businesses to try their hand at optimizing the most important step of the delivery process to meet customers' needs directly. Yet, this objective isn't the only catalyst. It also paves the way for cost reduction and profit margin optimization, ultimately bolstering the efficiency of the entire supply chain.
Within this context, a range of strategies stands ready to drive success:
#1 Implement technology-driven delivery models to address broader challenges
Even if it appears that factors such as inclement weather, traffic fluctuations, and evolving customer preferences might limit your control over the last mile, there's actually a significant opportunity to differentiate your service. This differentiation can be achieved by making improvements using technology-based solutions.
Here are some pivotal last-mile delivery solutions and the enhancements they provide:
- Last Mile Delivery Software: Specialized software solutions can greatly enhance the operational efficiency of last-mile delivery. Such software aids businesses in automating their processes, making real-time adjustments according to traffic and weather conditions, thus enabling on-time delivery and improving customer satisfaction.
- Route Planning Software: These tools don't just plot a course; they optimize your delivery routes, taking into account distances, current traffic conditions, and delivery windows. Their use can result in notable time and cost savings, and reduce wear and tear on your vehicle fleet.
- Real-Time Tracking and Analytics: Real-time visibility into the delivery process enables timely decision-making and quicker issue resolution. It not only ensures accountability but can help you spot trends and patterns, and adapt your operations for improved efficiency.
- Fleet Management Systems: Comprehensive solutions for managing your vehicle fleet, these systems can provide crucial data on vehicle usage, fuel consumption, and more. With this, you can ensure proper vehicle maintenance, likely reducing downtime and increasing overall fleet performance.
- Smart Communication Tools: These tools help maintain open lines of communication with customers, offering real-time notifications, estimated delivery times, and updates about their delivery status. This leads to improved customer satisfaction, reduced uncertainty, and more successful first-attempt deliveries.
#2 Balance environmental responsibility and profitability
For businesses in retail and transportation, addressing ecological and economic challenges should be as much a priority as driving their day-to-day operations. The increasing push from governments towards environmentally friendly delivery options is not to be taken lightly. Societal and consumer demand is shifting towards green, low-carbon, and energy-efficient logistics and distribution services.
As stated by Bernd Heid, a senior partner of McKinsey & Company:
“We see numerous technology and delivery chain solutions working independently. Our research shows, however, that in an 'ecosystem scenario' in which both public and private players work together effectively, delivery emissions and congestions could be reduced by 30% until 2030 when compared to a 'do nothing' scenario, and technology can help to bring delivery costs down by 25% at the same time.”
It's clear that an environmentally responsible approach isn't the only benefit companies can expect. 61% of companies emphasize sustainable practices mainly to realize cost savings, while 51% adapt their operations to adhere to evolving regulatory requirements. This indicates that the wave towards sustainability, fostered by broader collaboration and technological solutions, is a viable strategy that balances both environmental stewardship and profitability.
#3 Add some innovative delivery solutions
Per the insights from the Capgemini report, businesses are incorporating last mile delivery technology and strategies to effectively manage the complexities tied to delivery. These are some of the solutions being put into practice by leading companies.
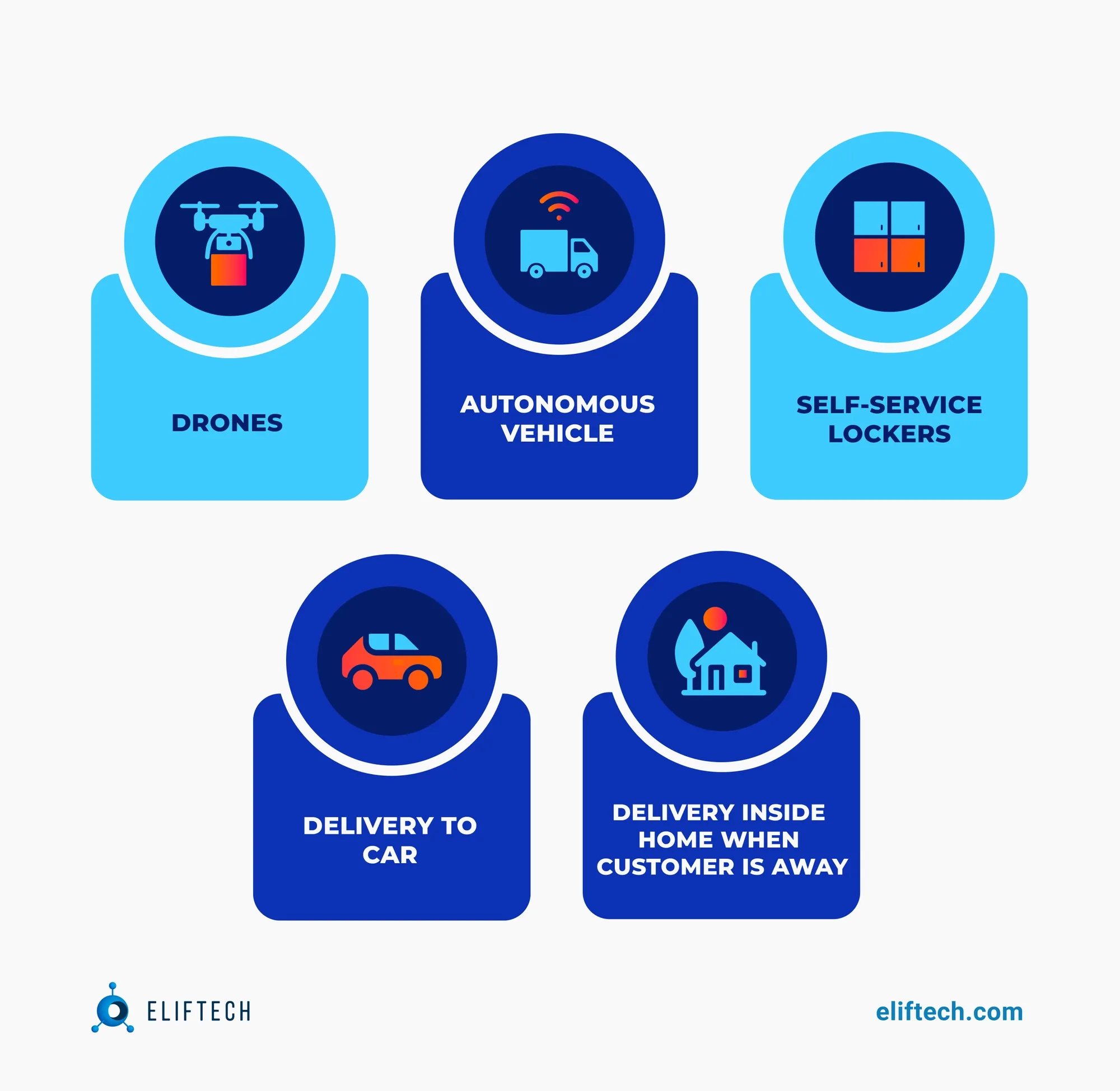
Self-service lockers. Customers can pick up their items at any time thanks to smart lockers placed in convenient locations such as malls or residential areas. Customers can retrieve their orders by entering a unique pick-up code, eliminating the need for human involvement in the process, thus minimizing costs. Amazon and Walmart are among the first retailers to practice this for the reasons you can see in the picture below.
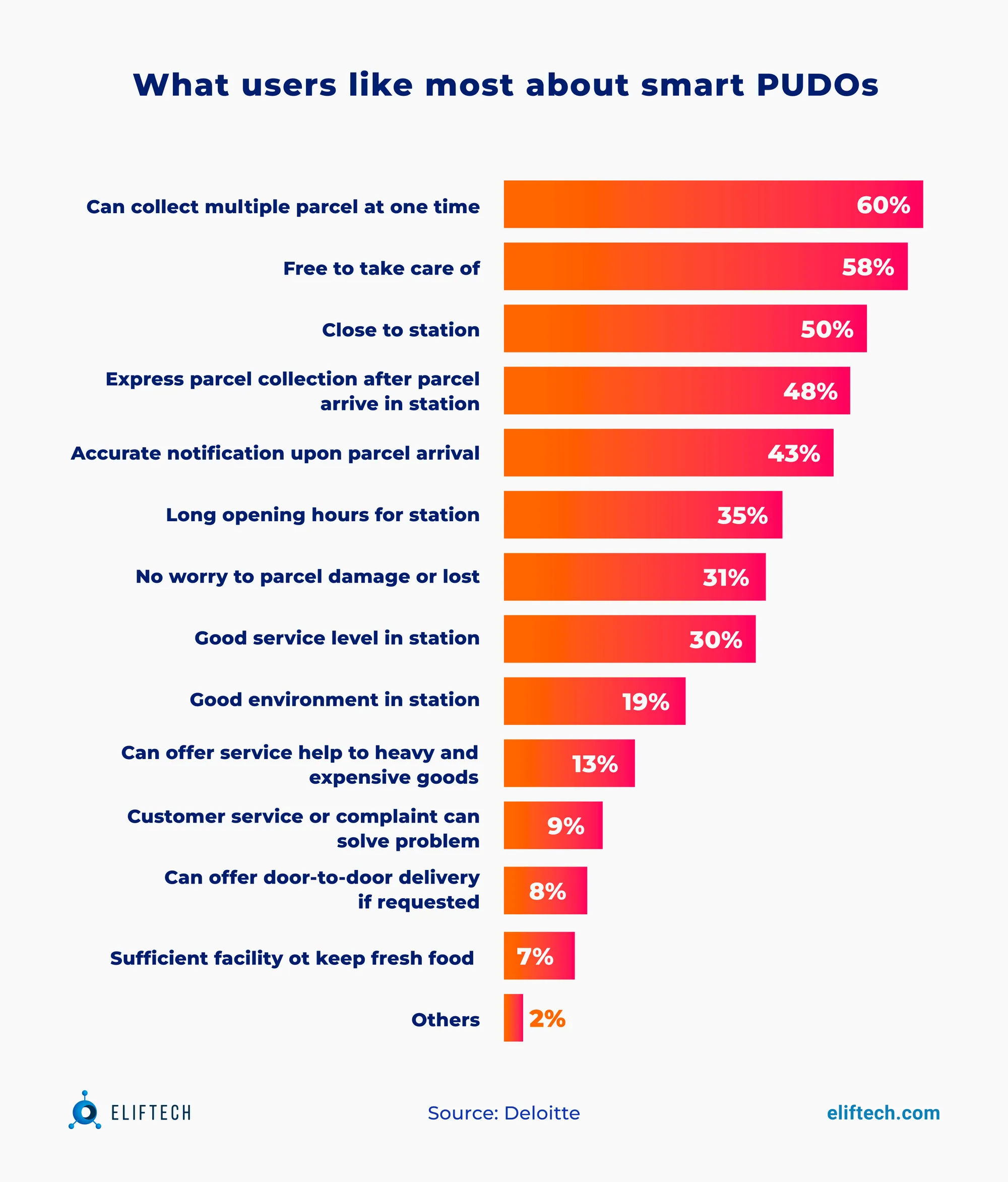
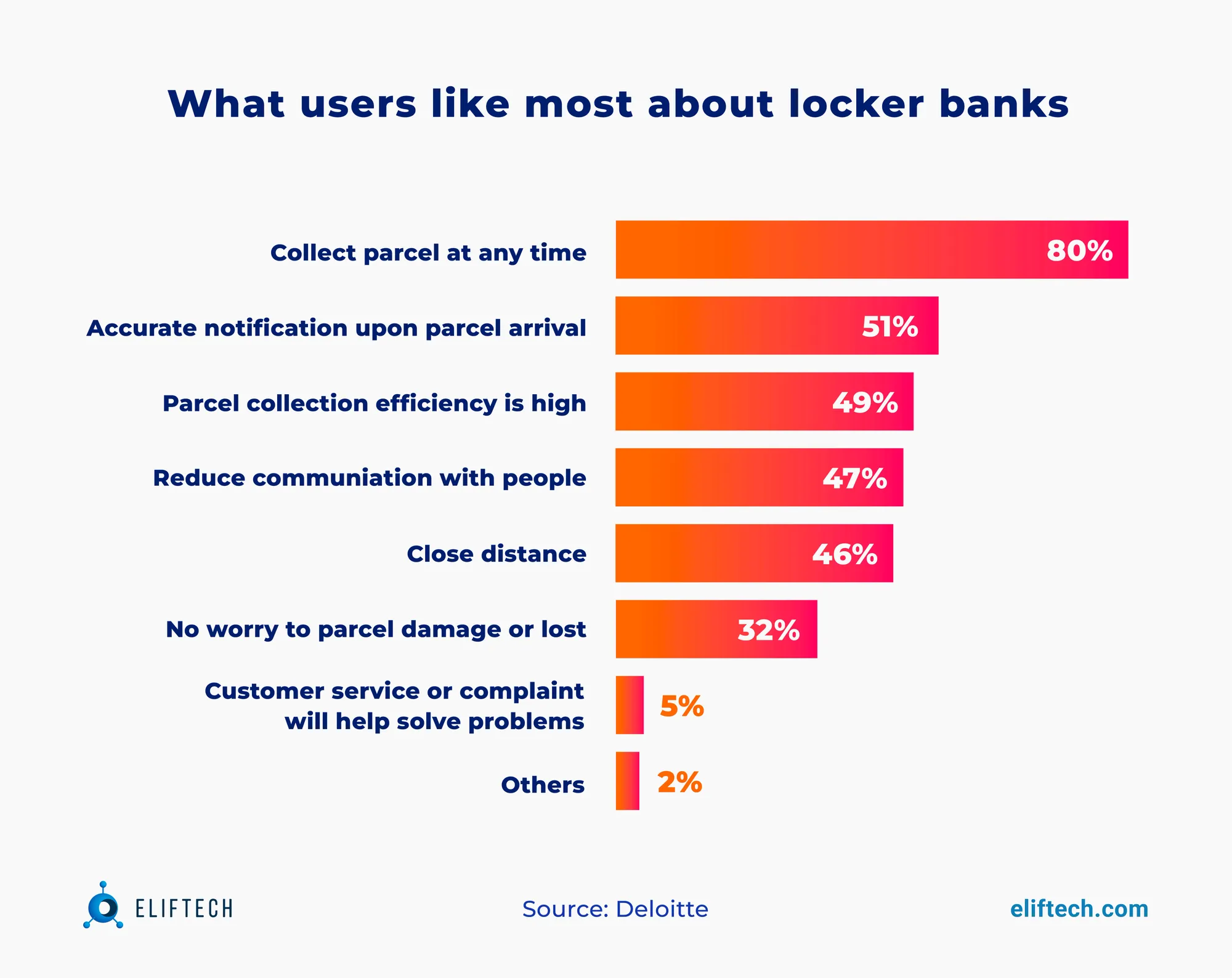
Smart locker banks. Contrary to self-service individual lockers, smart locker banks are a more extensive system of lockers organized in a central hub for package distribution and pickup. Delivery service providers use this strategy to streamline the last-mile delivery process, as it also helps them meet other delivery needs, for example, temperature-sensitive ones. Smart locker banks often include various locker sizes and may incorporate features like temperature control for storing perishable items.
In the picture below, you can also find what users like most about smart locker banks:
Drone delivery. Drones fill to meet the demands for the same-day and urgent delivery requests. They are exceptionally good for delivering parcels to urban and remote rural areas, ensuring minimum delivery time with maximum efficiency. Both American Amazon and JD, the largest retailer in China, are already experimenting with drone technology to enhance their last-mile delivery capabilities while also addressing distribution challenges in rural and remote areas.
Unmanned vehicles. This technology is relatively new and not properly tested for businesses, but will mainly shape the future of deliveries. Self-driving vans or robots navigate through neighborhood streets and deliver packages without the need for a human driver. This helps address numerous limitations in terms of cost, distribution efficiency, service quality, inability to get into the house, and regulation restrictions.
Delivery to the car. This type of delivery service grants couriers access to a person's vehicle, enabling them to make deliveries inside the vehicle. Amazon has launched this service in partnership with General Motors and Volvo.
Delivery inside the home. This delivery service allows couriers to enter a customer’s home and leave packages there. The Dutch supermarket chain Albert Heijn experiments with this service. This is usually done via IoT-enabled smart locks that allow the delivery person to gain access to the customer's home using a temporary access code or through a mobile app.
#4 Implement AI and IoT technologies to chance last-mile efficiency
The integration of AI (Artificial Intelligence) and IoT (Internet of Things) technologies within fleet management systems and other technological advancements is instrumental in optimizing last-mile delivery operations. These innovations assist businesses in cost reduction while ensuring a smooth and seamless customer experience.
Applications of AI in last-mile delivery
Effective route planning translates to notable cost efficiencies and operational improvements. The infusion of AI into route planning enables the calculation of optimal and cost-effective routes. AI-powered routing algorithms consider an array of variables, including weather conditions, traffic patterns, customers’ delivery time slots, driver schedules, and other priorities. This holistic approach is designed to identify the most optimal route, with a focus on minimizing driving time or recalibrating the route in real-time, as necessary.
Leveraging historical data encompassing successful and unsuccessful deliveries, idle periods, distance traveled, time per delivery, and fuel consumption, an automated approach is implemented to mitigate the risk of failed deliveries and reduce fuel expenditure. Drivers are empowered with real-time alerts, enabling them to navigate the most efficient routes with precision.
Application of IoT in last-mile delivery
Real-time tracking capabilities are part of a just-in-time (JIT) strategy commonly known in logistics for aiming to reduce inventory costs and minimize excess inventory storage. Thanks to such tracking technologies as barcodes, RFID, IoT, or GPS, it’s also easily possible to ensure real-time tracking and precise monitoring of delivery vehicles, offering customers up-to-date information on their packages' status and location by sending them automated notifications.
Furthermore, by integrating IoT sensors into packages and vehicles, businesses can achieve more than just real-time tracking. These sensors also enable the monitoring of temperature and environment, ensuring the safe transportation of temperature-sensitive goods. This capability helps address the challenge of products requiring special handling during delivery, providing a reliable solution for delivering perishable items or sensitive goods to customers.
In addition to real-time tracking and temperature monitoring, IoT technology finds applications in smart lockers and voice-activated access systems. Smart lockers offer secure and contactless delivery options, while voice-activated systems (e.g., Amazon Echo or Google Home) allow customers to place orders and grant access using voice commands, enhancing convenience and efficiency in last-mile delivery.
Read more: Logistic Tracking System: How to Optimize and Streamline Your Business Logistics?
#5 Keep the value of transparency for customers in mind
By implementing intelligent communication tools like last mile delivery tracking software or SMS notifications, companies can furnish customers with live updates regarding their package's status, estimated delivery windows, and possible delays. This proactive communication keeps customers informed, making them more likely to be present to receive the delivery. Consequently, this diminishes the instances of failed delivery attempts and the necessity for redelivery.
#6 Partner with leading technology companies and providers
Partnering with leading technology companies and providers like ElifTech is the best way for logistics companies to gain access to a wealth of resources and professional expertise in this field. Such collaboration allows access to advanced technologies including last-mile delivery software, data analytics, and innovative delivery options.
We’ve been in the industry for a long time, helping businesses enhance their last mile delivery tracking, implement route optimization algorithms, and integrate real-time communication tools to provide customers with transparent and efficient delivery experiences.
Discover how ElifTech's last mile delivery logistics solutions can help:
- Personalized last mile delivery apps for rapid delivery and consistent automated updates.
- Cloud and IoT integration for efficient operations and robust security.
- Comprehensive third-party and API integrations in last mile delivery platform.
- Streamlined processes and strategic insights through AI and machine learning in last mile delivery management software.
ElifTech creates 3PL software for last mile, targeting clients who value visibility, control, and automation. Contact us for a consultation to leverage our technical expertise for the strategic optimization of your 3PL platform.
