FinTech
How open banking boosts the U.S. FinTech sector?

According to the British research center Juniper Research forecast, by the end of 2022, the number of open banking users worldwide will double from 18 million in 2020 to more than 40 million. When it comes to open banking, the fintech landscape still seems in flux. However, in the coming years, the banking sector is expecting "uberization," as a result of which the number of personnel in the industry may be reduced by 50%. At the same time, profitability in some banking services will fall by more than 60%. What is open banking? How does open banking work? Read about the benefits, risks, regulations, and worldwide stats of open banking in 2022.
How the financial services market changes and what to expect
In America, the fintech industry is growing, and it became clear to financial institutions “what open banking is and how it works.” However, the American fintech market is at the initial stage of development, its structure still needs to be solidified, and banks are the main investors. Nevertheless, the number of fintech startups is growing, allowing us to discuss a good forecast. When diving into the question of “what is open banking,” consider that online banking, electronic payments, digital lending, and technological products for the insurance sector are priority areas.
Consumer Confidence in Fintech: Open the data or die!
In recent years, finance has been "digitized." The development of online banking, financial technology, and other services has created unprecedented opportunities for convenience and accessibility for customers. The events of 2020 have significantly accelerated the digitalization processes. In addition, the pandemic is forcing more and more people to use digital channels.
This global trend has affected, first of all, many traditional sectors, in particular banking. Against the backdrop of Covid-19, there was a growing understanding that today, few organizations will act in isolation: to survive in a competitive environment, banks need to use relationships with external partners to diversify their products and expand coverage to new customer segments.
Global fintech market
Companies operating in technological innovation in financial services usually try to improve the existing economic infrastructure or create a new one. As a rule, they directly compete with banks. If you’re looking into “what is open banking,” check out EY's Fintech Adoption Index. According to this research, nearly a third of consumers use two or more fintech.
The most popular fintech services are
- Online payments (used by 50% of respondents)
- Auto and health insurance benefits (24%)
- Investment and capital raising applications (20%)
- Online loan platforms (10%)
- Financial instruments (10%)
The Executive Director of G.R. Capital venture fund says that the unbundling of the financial market is taking place now: the traditional bank format is being replaced by hundreds of technological products and services. Startups are winning this market because they provide the best user experience and focus on solving a specific problem.
Fintech geography
Let's explore “what is open banking” by looking at the number of users of fintech services. Currently, the penetration rate of fintech services in the U.S. is only 33%. At the same time, in 2021, out of 27 global fintech companies with a capitalization of $1 billion ("unicorns"), 14 startups are incorporated in the United States, eight in China, and five in other countries of the world, according to Visual Capitalist. The volume of global investments in the industry grows annually by almost 50%. According to Deloitte's “Investment banking digital transformation”, the value of the investment in the sector has grown from $1 billion in 2008 to $24 billion in 2022.
According to CB Insights, the number of mega-round investments of more than $100 million in the North American region has grown from one deal in 2013 to 20 deals in 2022, a record number of annual mega-round checks worldwide. Trends, Adoption, and Investment show that the average adoption rate of fintech projects worldwide is 33%. The U.K. leads the way with 42%, followed by Spain (37%) and Germany (35%). Slightly less receptive to fintech are Switzerland (30%) and France (27%). At the same time, the European fintech market is inferior to the American one regarding investment volume and the number of transactions.
Fintech services that have changed the industry forever
The financial services market size is about $25 trillion annually, so fintech startups are trying to take a bite out of this pie. As a result, the number of nascent fintech projects is at an all-time high — many players are striving to take place in a promising market. As a result, despite the industry's relative youth, many of yesterday's financial startups have become influential market players.
- LendingClub is a service that connects borrowers and lenders in the United States. The startup promises to lower rates, opening the loan market to more participants and increasing competition.
- Karma is a bank providing online services. It specializes in payment solutions for online stores and credit payments, such as processing merchant payment requests and customer payments. In addition, the company acts as a "buffer," reducing risks for buyers and sellers.
- Robinhood is a mobile stock trading app that allows its users to buy and sell shares without any fees. In addition, the app offers exchange brokerage services for investments in public companies and U.S. exchange-traded funds.
- Credit Karma is a service that calculates your personal credit rating and helps you improve your financial situation. The rating is free, but there are other product ads in the app.
What is open banking, and how does it work?
In case the issue of “how does open banking work” seem confusing, here’s an infographic:
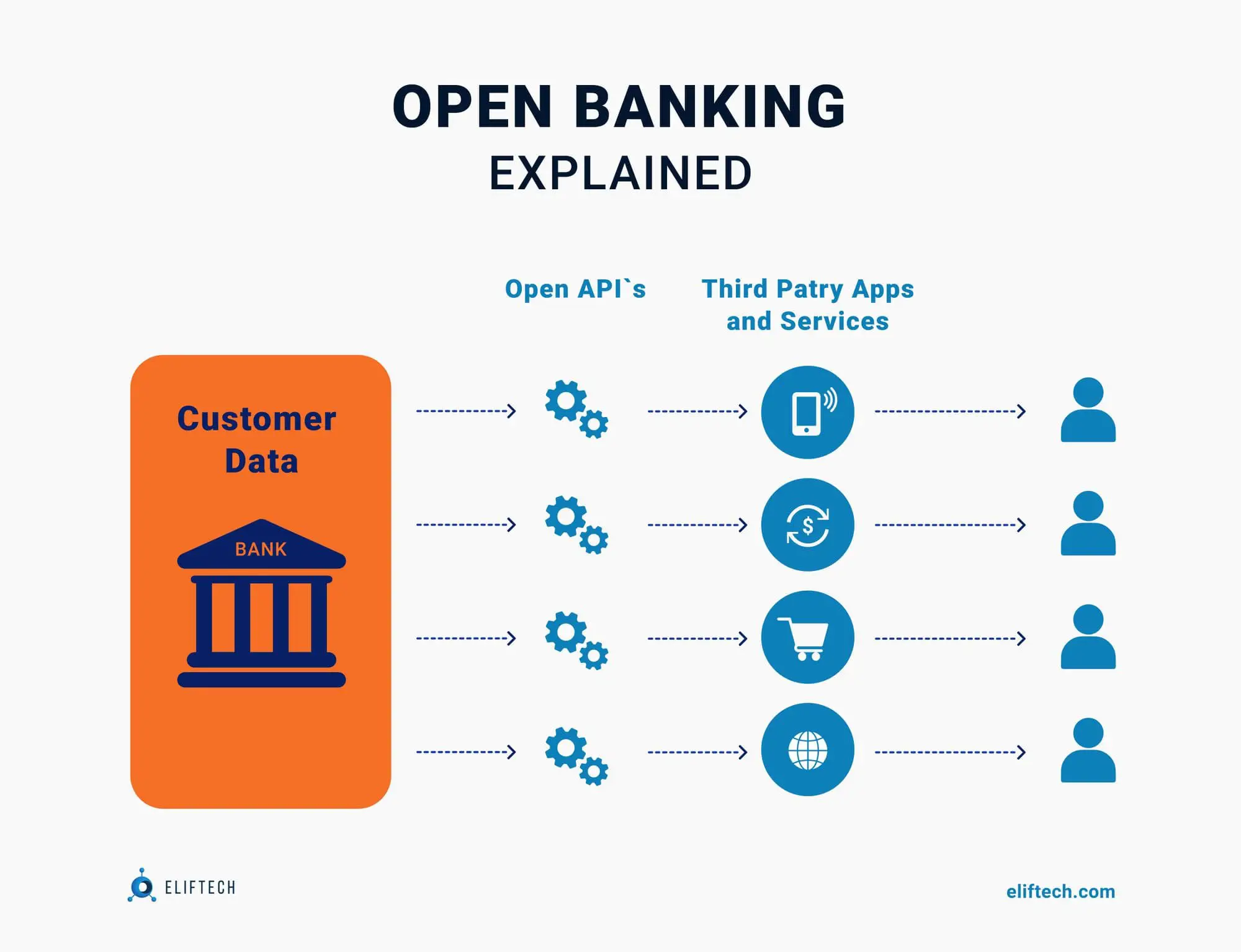
Open banking is a system that allows banks to share their application programming interfaces (APIs), making it possible for third-party companies to access the financial information they need to develop new applications and services, which ultimately empowers account holders with greater financial options. In addition, open banking enables fintech companies to build more advanced solutions for managing personal finances and forces traditional operators to improve their offerings or collaborate with third-party organizations. Thus, open banking promotes the development of competition in the banking sector.
APIs are a certain set of codes and protocols that define how different software components should interact. They allow various applications to interact with each other. Because of open banking, APIs are now used to pass commands to third-party providers. APIs are also necessary for Banking-as-a-Service functioning. BaaS is an end-to-end process connecting companies to banks' systems directly through APIs.
Benefits of open banking APIs are boosting financial service innovation
Open banking can expand banks' customer reach - an opportunity that traditional banks cannot ignore. It can also create revenue-sharing ecosystems, where traditional operators provide customers with access to third-party services, earning revenue from a subscription or referral base. In addition, open banking allows financial institutions to commercialize their infrastructure by shifting into the BaaS space.
When analyzing the question “how does open banking work,” it is reasonable to focus on open banking benefits.
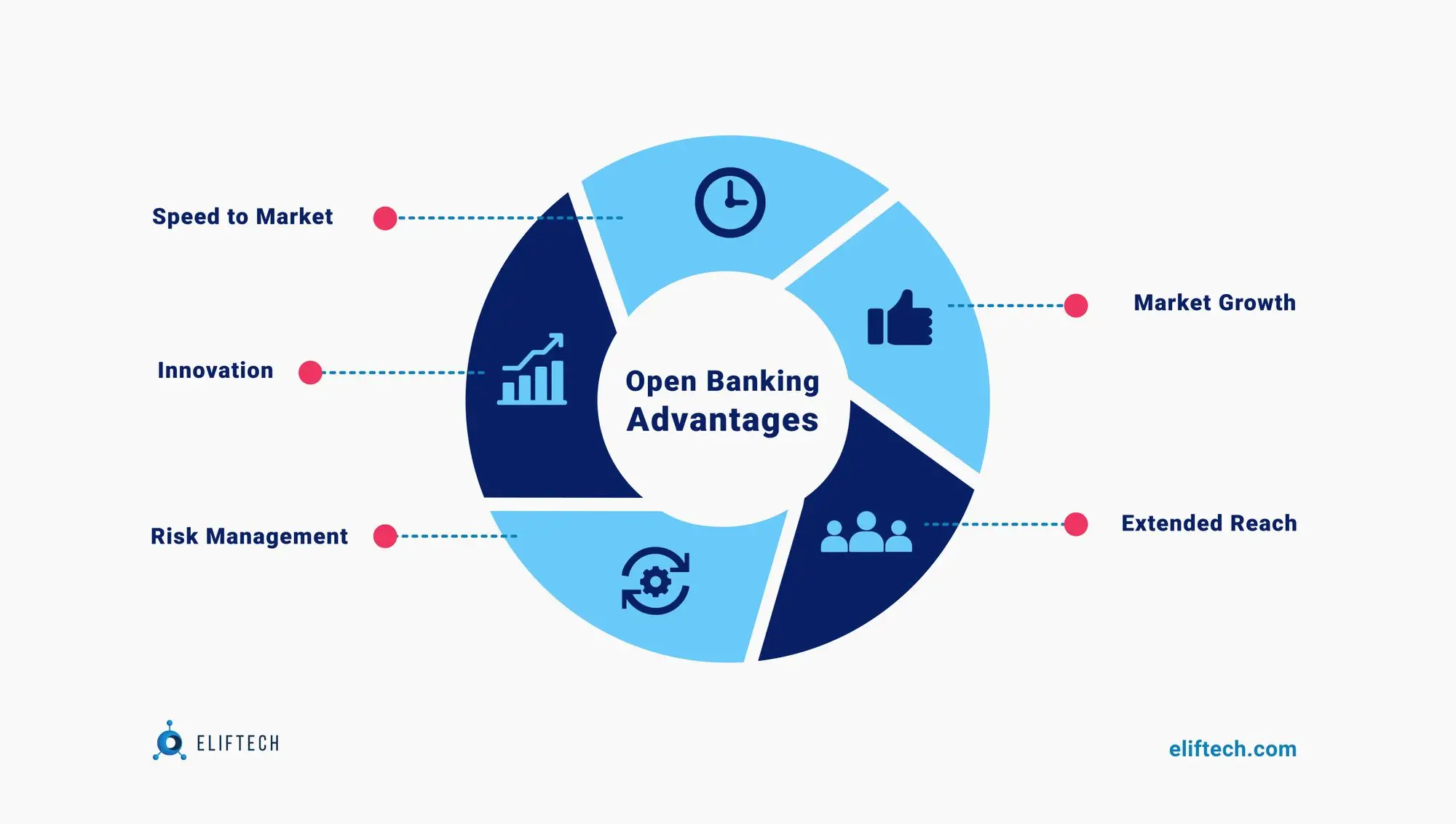
The main advantages of open banking include the following:
- Pressure on banks: Open banking is believed to provide more benefits to fintech companies and third-party organizations, but banks are incentivized to improve their services.
- Additional useful tools: App developers will find it easier to work with open APIs, allowing them to help you control your costs. With the help of artificial intelligence, they can predict your behavior and recommend products that will help you save money.
- Simplification of obtaining a loan: Getting a loan or refinancing can become easier. Instead of manually gathering information from various sources and providing it to a potential lender, consumers can let lenders simply get all the data in one place.
- Business loans: Lenders may want to check your books when your small business needs a loan or, for example, a line of credit. Again, instead of sending a bunch of reports, lenders can get all the data they need from your bank and accounting system.
- Decreasing the cost of payments: Payments are an important part of European open banking regulation. According to the European Commission's Second Payment Services Directive (PSD2), banks must allow third parties to initiate payments on their behalf. This isn't necessarily something new (Venmo and PayPal are popular non-bank products), but it will make processing payments easier – and cheaper.
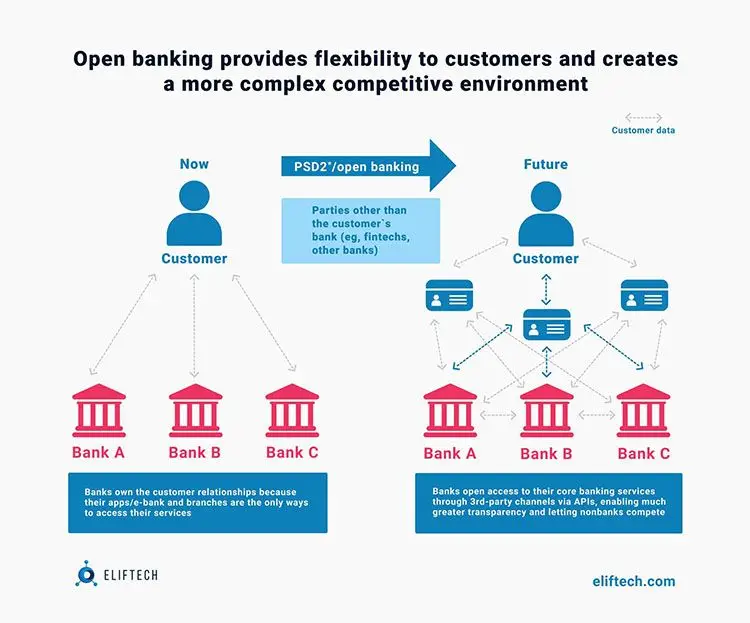
From the client's point of view, open banking provides the following benefits:
- Single window principle. Users can manage personal finances and analyze accounts from different banks on one platform.
- More friendly and simple interfaces. As technology companies and fintech startups get involved in financial services, clients receive more user-friendly interfaces and new tools.
- More companies on the market → more competition → more profitable offers for customers.
- It is easier to get loans, as open banking speeds up data analysis and increases the transparency of scoring.
- Personalized approach to the client. As financial institutions access customer data, they can conduct a deeper analysis of their financial habits and behavior.
For banks and fintech companies, the concept also provides many advantages:
- Revenue growth occurs due to the expansion of sales channels and the emergence of new services.
- More inquiries are converted into sales. A more personalized approach to customers ensures conversion growth.
- Increasing customer engagement and retention.
With the widespread use of open banking in the financial sector, competition is expected to grow, and the role of banks will weaken. And this helps to achieve the main goal of the concept - the development of new financial services and their increased access to people. In practice, the development of open banking has taken different paths in different parts of the world.
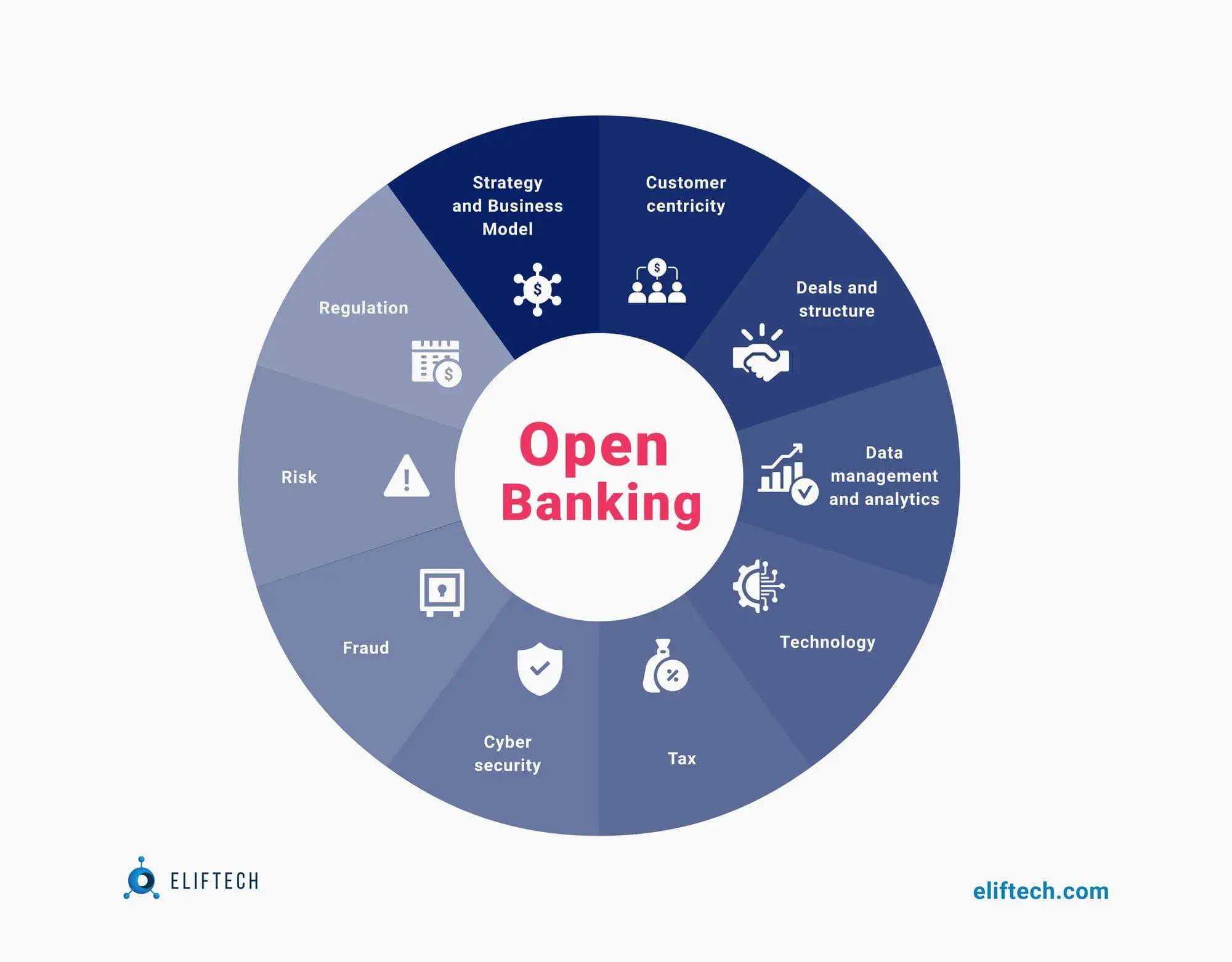
Risks of Open Banking: Avoid pitfalls
Without deviating from the topic, let's talk about the security of open banking and what you should pay closer attention to. After all, with the growing popularity and spread of open banks, attackers are looking for new loopholes and vulnerabilities. As a rule, the targets for cyberattacks are:
- API
- Mobile applications
- The infrastructure of fintech companies
- Users
Let's take a closer look at each point.
Attackers can connect to the automated system with the help of API. In addition, many banks still pass sensitive information in their API URLs. Parameters such as passwords, email, etc., may appear in the logs, be displayed in the browser and browsing history, and become visible to devices that intercept SSL.
When it comes to mobile apps, SDKs (software development kits) are a danger. There were many examples when initially innocuous applications became malware. These "hidden features" can backfire, especially regarding financial data and personal information.
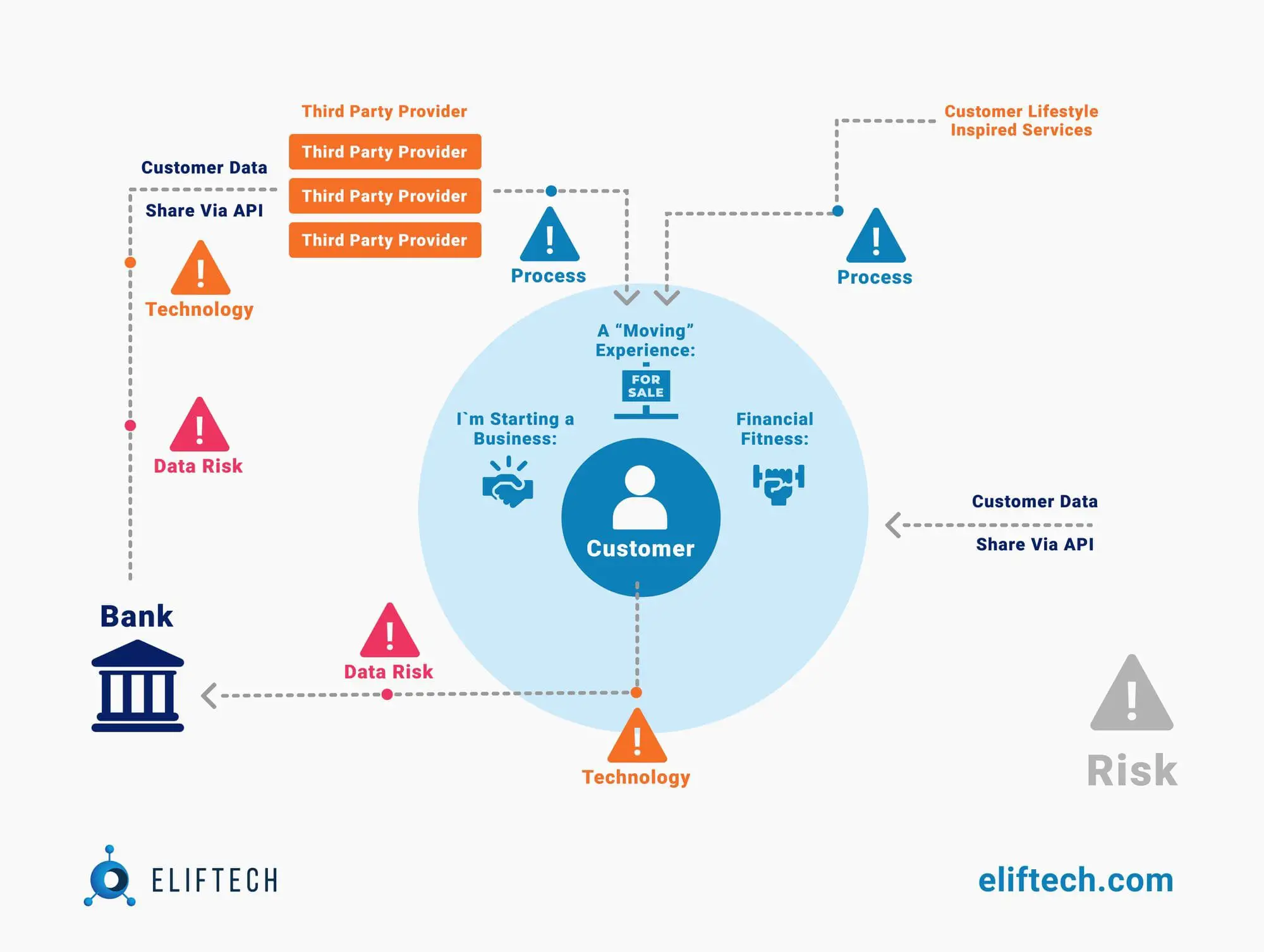
Fintech projects are most often implemented using cloud technologies. This adds a cloud service provider to our long chain of participants in processes with Open API. Unfortunately, hackers can infiltrate the provider's network and influence several fintech companies. Users and banks should know about the issue and risks.
The simplest and cheapest attacks are against users. In 2022, you won't surprise anyone with phishing in the context of an ordinary bank, and it's more complex with open banking. This is because the user is aware of a large chain of intermediaries in advance and may be too trusting. As a result, some scammers go to great lengths to create fake apps that are then placed on marketplaces.
Making open banking safe: Better data security
Only an integrated approach to security provides sufficient system resistance to threats. The fintech industry is no exception. A mandatory requirement of the PSD2 regulator is multifactor authentication. According to Microsoft, it prevents 99.9% of account hacking attempts.
Open Banking also recommends using FAPI, an interface based on OAuth 2.0. It is a more secure version of OAuth 2.0 and allows you to provide access to services without user data with the help of tokens. In this case, the token can be revoked at any time. Fintech companies need to pay attention to the protection of infrastructure. It is worth securing cloud systems, checkpoints, and development mechanisms. This closes the remaining loopholes for hackers.
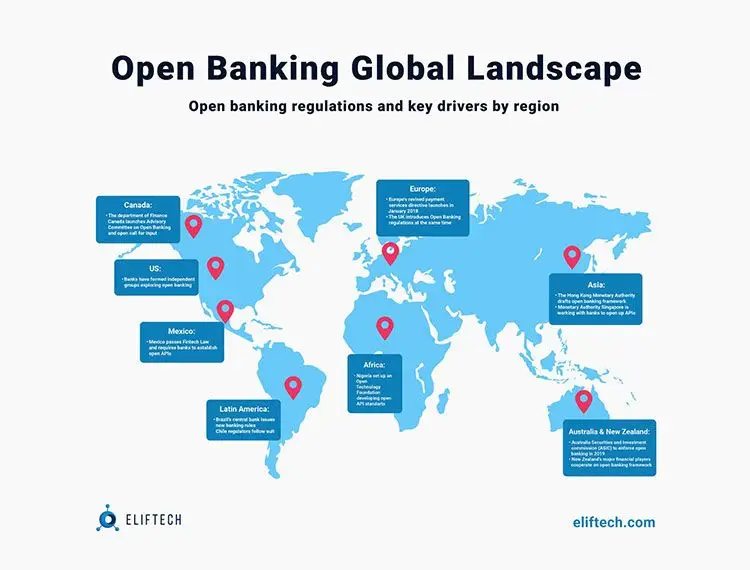
Open banking regulation in the U.S. and worldwide
Because open banking ultimately results in competition, many financial institutions are reluctant to take the necessary steps. Therefore, regulating this industry has become a key factor in spreading open banking in many countries.
In the U.K., regulators have ordered nine of the largest retail, small and medium-sized business account operators to use open APIs. It allows third parties to access the data the customers agreed to share and initiate payments from customer names.
In countries with less developed legislation in open banking - including the USA, Japan, and Canada - available banking services will probably continue to develop only due to consumer demand and under competitive pressure.
Regulation of fintech activities in America
U.S. payment laws consist of various regulatory regimes administered by state and federal regulators. The main purpose of these regimes is to protect consumers, promote the orderly and efficient transfer of funds, and prevent money laundering and other illegal activities related to payments. In addition, at the federal level, the regulation of fintech services in the States is related to several laws and regulations in the financial industry, including:
- Consumer Credit Protection Law.
- Bank secrecy law.
- Gramm-Leach-Bliley law.
- Electronic Funds Transfer Law and Reg. E, Dodd-Frank Act.
- Law on the accelerated availability of funds.
- Reg. CC, Reg. J, Reg. II.
- Uniform commercial code.
At the state level, this sector is usually regulated by money transfer laws. The federal and state legislative regimes governing payments are reinforced periodically by rules and guidelines from regulators. In the United States of America, open banking is not mandated by law. For a couple of years, it wasn’t apparent “how open banking work.” However, open banking concepts are becoming mainstream due to consumer and business preferences for faster and more efficient digital financial services.
While prudential regulators such as the FDIC have issued guidance on open banking and the use of third-party service providers by banks, no specific rules for open banking have been adopted. Therefore, open banking remains subject to contractual requirements negotiated between third-party service providers.
Open banking examples and use cases
Why is open banking the future of fintech? Back in 2018, the large Spanish and international bank BBVA launched its open platform. It uses APIs that allow third parties to offer financial products to customers without the need to provide a full set of banking services.
Connected Money allows customers to view various bank accounts along with loans, mortgages, and credit cards in one place. Barclays is announcing its success in the open banking market as the first U.K. bank to enable account aggregation within its mobile banking app. As a result, the bank's customers can view their accounts in other banks in the Barclays mobile application.
Open banking market evolution or revolution?
One more answer to the question of “Why open banking is the future of fintech” is the fact that since 2019, there has been an increase in digital transformation that affects all industries, including finance. Banks improve the quality of customer service and solve fraud and cybersecurity issues. Customers, in turn, expect more control over personal data from financial institutions. Open banking just appeared to give customers and financial institutions complete control over their data.
- Open banking is a concept that allows you to exchange data within the financial market using an open API. Open banking stimulates the emergence of new solutions in the market and increases competition. This improves the quality of service in the financial industry due to the greater involvement of market participants.
- Open banking reduces the time for setting up the API, speeds up the process of obtaining data, and makes it quite easy to perform transactions between different banks.
- Thanks to open banking, fintech companies can access user data from any bank. Note that the user may not share their personal data. In addition, new products can be developed based on information that fintech companies receive, such as account numbers, transaction histories, etc.
The personal data of users and their subsequent analysis open up great opportunities for the financial industry in the direction of personalization of services. Furthermore, the demand for such services drives fintech companies to develop new products to solve business needs.
So in the USA, it was developed a platform for managing finances and tracking expenses. The most interesting thing about Mint, as the platform is called, is the availability of personalized offers for users.
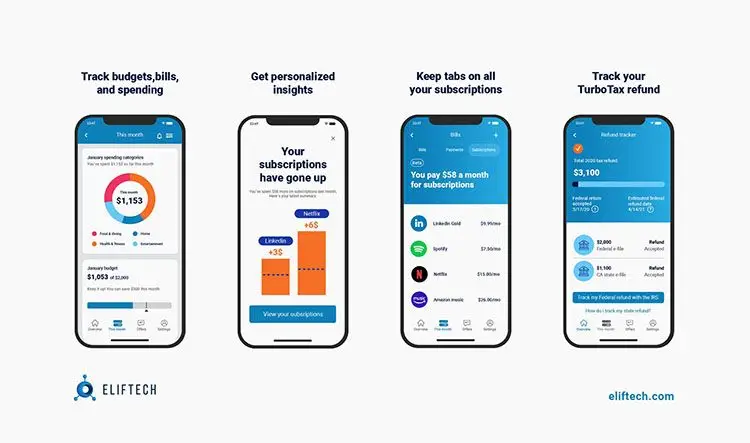
It is also worth mentioning the European service Chip, which contains offers regarding savings accounts. The application automatically accumulates savings and selects favorable user rates depending on their needs.
Let's also have a look at the British development called Sync Money, which exponentially uses the possibilities of open banking.
Clients can use the application to manage their accounts, exchange currencies, and transfer to banks and other financial institutions. By the way, the U.K. proposed the concept of open banking back in 2015.
The bottom line: Fintech industry trends and new tools
A closer look at open banking makes the fintech landscape seem extremely vast. Indeed, over the past ten years, technology has dramatically changed how the financial sector works. The spread of smartphones and the Internet allows the creation of new business models and interaction patterns between financial institutions and customers. We compiled a list of fintech trends that will develop over the next few years.
- Getting financial services using a mobile phone. Making financial transactions using a smartphone is convenient and accessible from anywhere in the world. Smartphones are used by 59% of the planet's adult population.
- Social networks for the provision of financial services. Social network users report much about themselves: a place of work, interests, friends, relatives, etc. Algorithms analyze this information to provide personalized financial services.
- Using chatbots to make a payment or other transaction without leaving the social network is convenient and easy.
- Alternative payment methods. Contactless payments, payments using terminals, and Q.R. codes.
- Credit marketplaces and user-to-user loans. Digital platforms connect borrowers, non-bank lenders, and private investors. In addition, the system allows people who cannot get a loan from a bank to receive credit funds.
- Big Data and A.I. technologies. Bots with artificial intelligence are learning and will soon be able to serve even non-standard customer requests independently. Big data and A.I. also help prevent fraud.
- Digital and biometric identification. Customer identification and authorization is one of the financial institutions' most important tasks. User identification by voice, fingerprints, and face recognition is changing the perception of reliability and security in financial transactions.
It may seem that traditional banks are irrevocably losing out to financial startups. However, big players are introducing new technologies to avoid losing the market. In addition, unlike startups, large companies have the time and resources to launch innovative products. For example, Capital One has embarked on a strategy to transform from a bank into a software development company that will also create fintech products. Along with this change, the company is undergoing corporate culture and hiring shifts.
Banks and financial corporations are also actively investing in fintech startups. According to American Banker, 82% of U.S. commercial banks plan to increase the volume of fintech investments in the next three years. This trend will spread to the world in the next ten years, and banks will claim the title of the key player in the global fintech market.
Neobanks offer users the conveniences and opportunities that traditional banks do not have, thereby increasing the number of customers. They provide a higher level of card security. For example, a physical card of a bank from Hong Kong MOX indicates only the holder's full name. Other data can be accessed in the application. This ensures that no stranger is using your card for online payment.
Experts believe that the model offered by neo-banks - services in a convenient virtual format - is becoming the standard in the financial industry. An important feature of neo-banks is their flexibility and adaptability, which helps them stay ahead of traditional banks. For example, U.S. startup Chime found that customers use debit cards rather than credit cards, but credit scores are important to them. This information allowed the company to launch a hybrid product combining debit and credit functions.
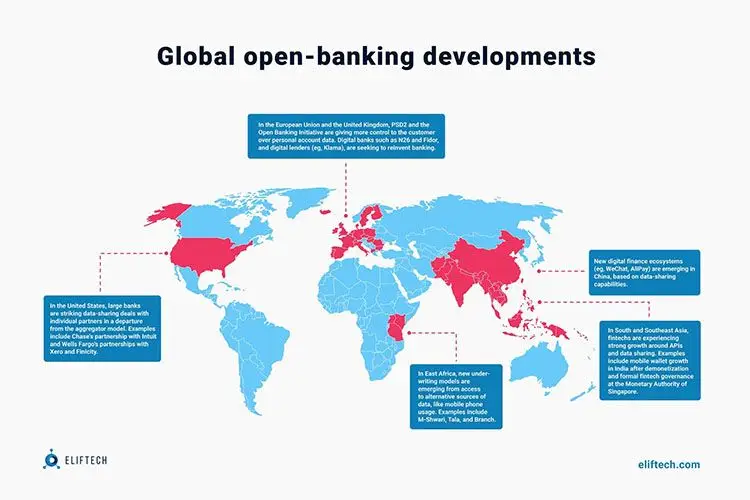
The development of open banking in the world goes in different ways depending on the following two factors:
- The regulator’s position and the availability of the documents regulating the related procedures. In this sense, the regulator can become either a driver or a limiter of growth.
- The situation on the market and its readiness for the development of open banking. This factor is decisive.
As we can see, in Europe and the USA, the market is "warmed up" for the active development of open banking, and new interesting projects are emerging there. On the other hand, in the countries of the Asia-Pacific region, the trend is just beginning to "swing."
Considering open banking as the future of fintech and your business in particular? Contact our team for a consult.
